Create MVC Application for Data Annotation Demo
Now, we need to create an MVC application for the data annotation demo. Create a new MVC application and inside the model, folder add a new class for model.
Right, click on model, click on add, and select class.
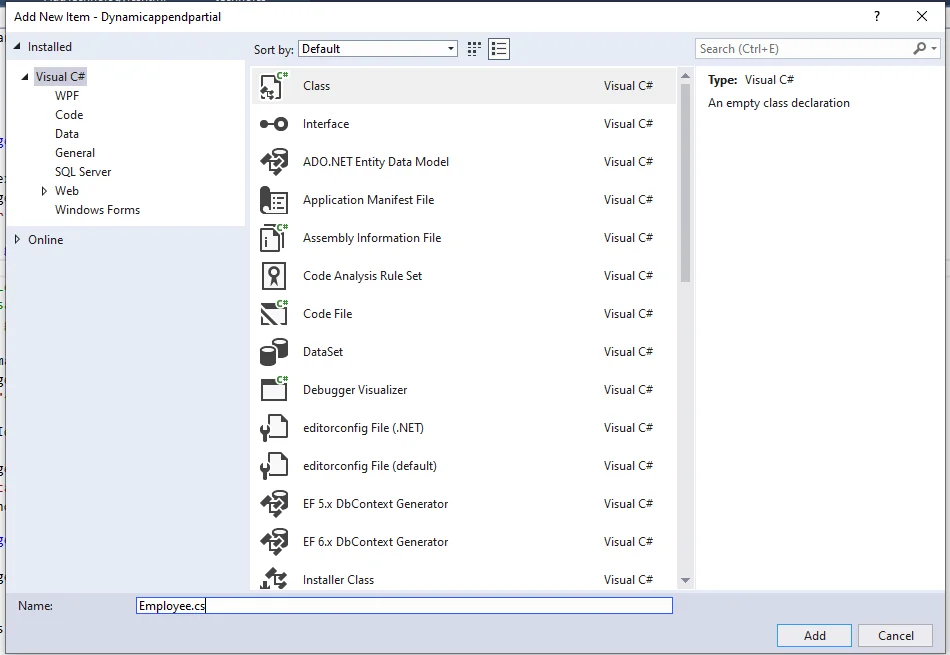
[Fig:- class for model]
Employee class
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace Dynamicappendpartial.Models
{
public class Employee
{
public int E_Id { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "name Required")]
[Display(Name = "Full Name")]
[MaxLength(30), MinLength(10)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "gender Required")]
public string Gender { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Email Address Required")]
[Display(Name = "Email Address")]
[EmailAddress]
public string EmailAddress { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Postion Required")]
public string Position { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Hire Date Required")]
[Display(Name = "Hire date")]
[DisplayFormat(DataFormatString = "{0:dd.MM.yyyy}")]
public DateTime HireDate { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "salary Required")]
[DataType(DataType.Currency)]
[Range(15000, 60000, ErrorMessage = "salary must between 15000 to 60000")]
public int Salary { get; set; }
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Website Required")]
[Display(Name = "Personal Website")]
[Url]
public string WebSite { get; set; }
}
}
Add controller inside the controller folder.
EmployeeController
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Mvc;
using Dynamicappendpartial.Models;
namespace Dynamicappendpartial.Controllers
{
public class EmployeesController: Controller
{
private PartialDbContext db = new PartialDbContext();
public ActionResult Index()
{
return View(db.Employees.ToList());
}
public ActionResult Details(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
Employee employee = db.Employees.Find(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(employee);
}
public ActionResult Create()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult Create([Bind(Include = "Id,Name,Gender,EmailAddress,Position,HireDate,Salary,WebSite")] Employee employee)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
db.Employees.Add(employee);
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
return View(employee);
}
public ActionResult Delete(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return new HttpStatusCodeResult(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
Employee employee = db.Employees.Find(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return HttpNotFound();
}
return View(employee);
}
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public ActionResult DeleteConfirmed(int id)
{
Employee employee = db.Employees.Find(id);
db.Employees.Remove(employee);
db.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
}
}
Right-click on Create method and add the view for create method.
Create view
@model Dynamicappendpartial.Models.Employee
@{
ViewBag.Title = "Create";
}Create
@using (Html.BeginForm())
{
@Html.AntiForgeryToken()
}
@Html.ActionLink("Back to List", "Index")
Now, run the application and click on create and add details and check the model validation
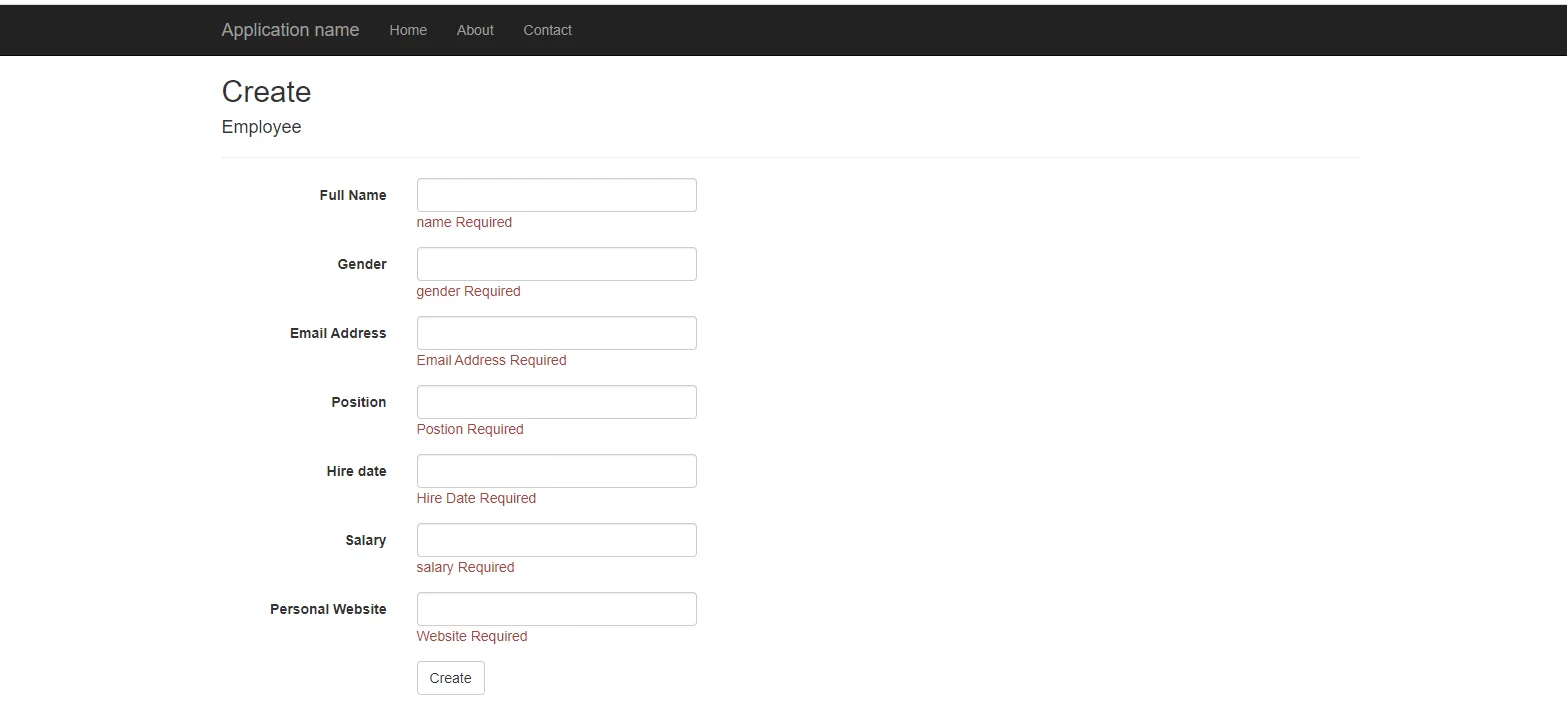
[Fig:- model validation for empty field]
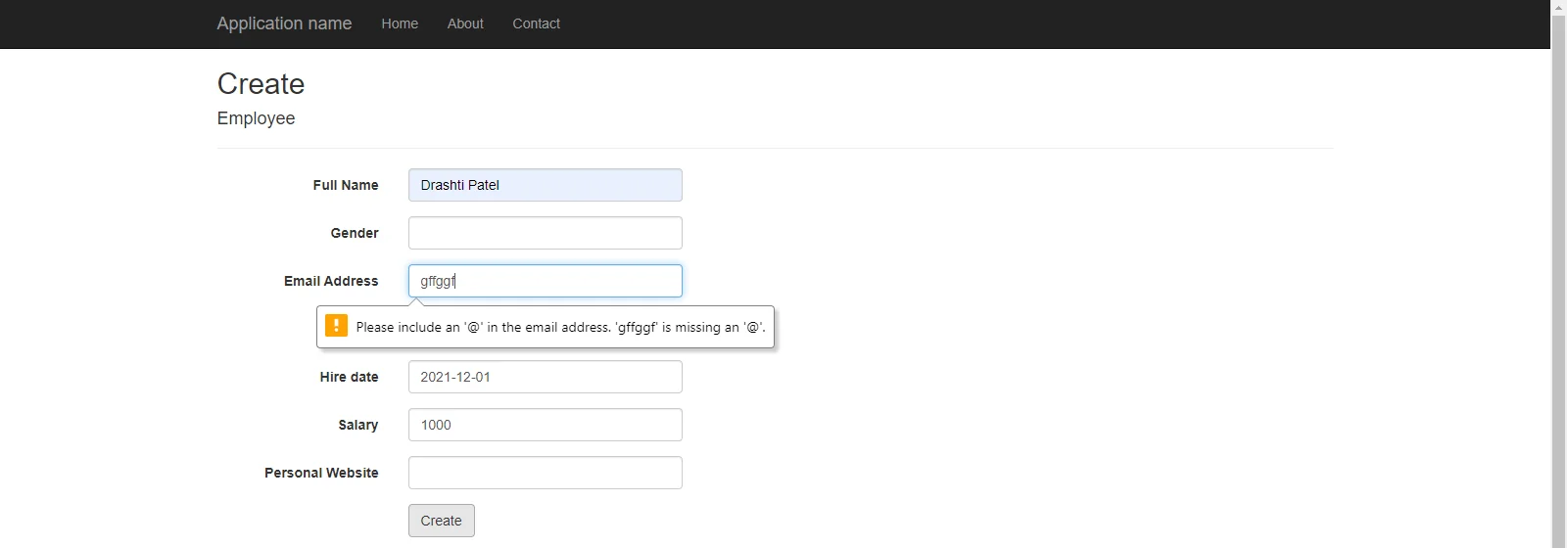
[Fig:- Model validation for Email]
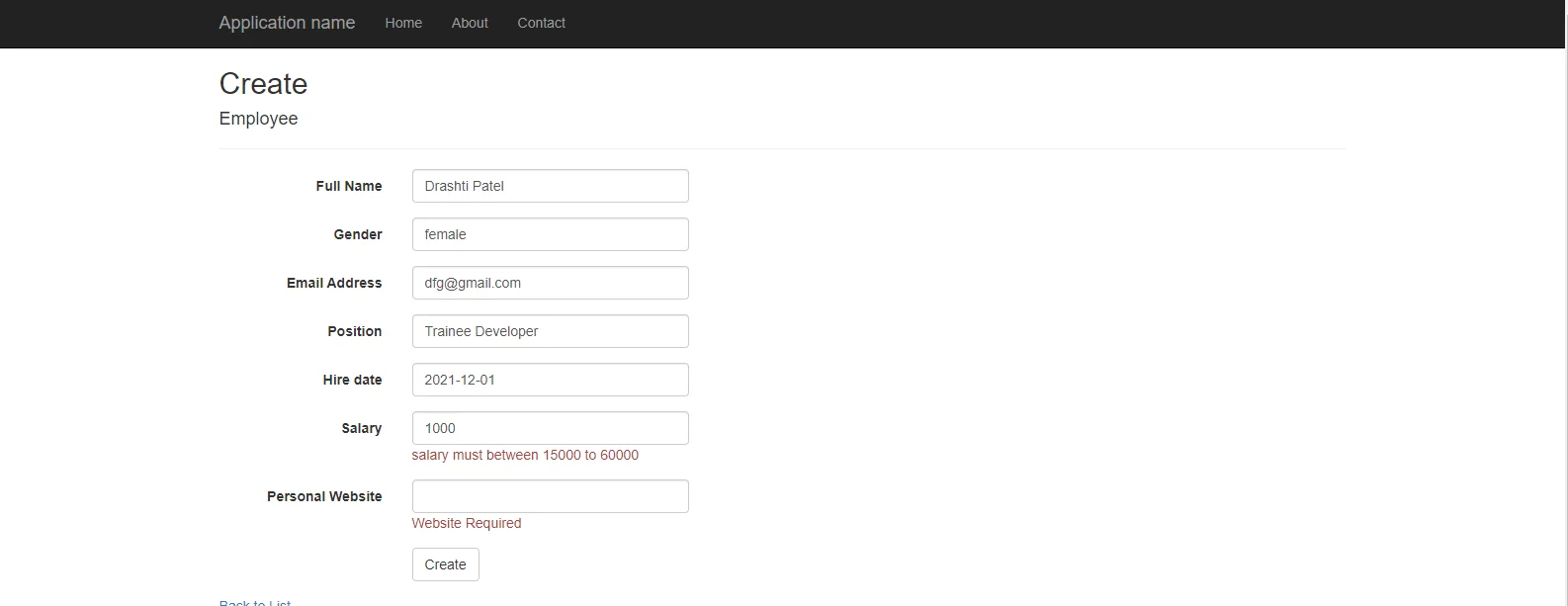
[Fig:- Model validation for a salary]