What is Swagger?
Swagger is one type of platform that provides the facility to access API data.
In this detailed technical document,we will learn how a web service can reply to web requests from clients such as browsers.
Swagger is a popular framework which is used to describe the structure of your API so that machines can read them. It is used widely by many ASP.Net software development companies across the globe.
API helps you to find the root of the application very easily.With the help of swagger APIs structure, we can automatically build beautiful and interactive API documentation.
What is the use of Swagger?
Swagger is one type of platform that is used to Run API and check Authentication System.The Swagger is the most popular and the most powerful HTTP client for testing the restful web services
Example of Swagger Step by Step
- For implementing swagger in ASP.Net Core, first, we will create a new project. For creating a new ASP.Net Core Web API, we will open Visual Studio 2019. Once Visual Studio is open, we will select the menu option File -> New -> Project.
- Once the new project creation window pops up, do select the ASP.Net Core Web Application,and click the Next button.
-
In Visual Studio please go with this process:
Select project in Solution Explorer click -> Manage NuGet Packages - Enter Swashbuckle in the search box - Check “Include prerelease”->select the package Swashbuckle package and then tap Install.
- This is used for generating Swagger documents for Web APIs that are built with ASP.NET MVC
1. Enable XML Project
Go to the Project ->Right-click the project in Solution Explorer and select Properties
Delete the "bin\Debug" from the path, and get the XML file directly from Solution Folder,Add Link.
Browse and Select the file -> Click on the dropdown arrow next to the ADD button - Select "Add as Link" (Adding the file as Link, will not copy the file to the project)
2. Configuring Swagger in Startup class
Now, it is time to configure Swagger inside of the Startup class. For this purpose, I would update the ConfigureServices to add Swagger.
Action Result, we will use the SwaggerGenOptions and call the method SwaggerDoc on it. The SwaggerDoc method takes two parameters
Add Below Code in Startup file
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.HttpsPolicy;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Options;
using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens;
using Swashbuckle.AspNetCore.Swagger;
namespace JWTSwaggerPracticalExam
{
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// ConfigureService Add the JWT services
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSwaggerGen(c =>
{
c.SwaggerDoc("s1", new Info
{
Version = "s1",
Title = "MyAPI",
Description = "Testing"
});
c.AddSecurityDefinition("Bearer", new ApiKeyScheme()
{
Description = "JWT Authorization header {token}",
Name = "Authorization",
Type = "apiKey"
});
c.AddSecurityRequirement(new Dictionary>
{
{"Bearer",new string[] { } }
});
});
services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidateAudience = true,
ValidateLifetime = true,
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
ValidIssuer = Configuration["Jwt:Issuer"],
ValidAudience = Configuration["Jwt:Issuer"],
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Configuration["Jwt:Key"]))
};
});
services.AddMvc();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(c =>
{
c.SwaggerEndpoint("/swagger/s1/swagger.json","MyAPI");
});
//if (env.IsDevelopment())
//{
// app.UseDeveloperExcepti config;
}
[AllowAnonymous]
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Login([FromBody]UserData login)
{
IActionResult response = Unauthorized();
var user = AuthenticateUser(login);
if (user != null)
{
var tokenString = GenerateJSONWebToken(user);
response = Ok(new { token = tokenString });
}
return response;
}
This method was created with the Token in JSON Format.This token is usedto verify the authentication whether the Username or Password is Matching or not.
If not, then this method could have issues and need to rectify.
private string GenerateJSONWebToken(UserData userInfo)
{
var securityKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(_config["Jwt:Key"]));
var credentials = new SigningCredentials(securityKey, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
var token = new JwtSecurityToken(_config["Jwt:Issuer"],
_config["Jwt:Issuer"],
null,
expires: DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(120),
signingCredentials: credentials);
return new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(token);
}
From the below code you can notice the basic key added in appsettings.json. You can also add it according to your choice,
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"profiles": {
"IIS Express": {
"commandName": "IISExpress",
"launchBrowser": true,
"launchUrl": "swagger",
"environmentVariables": {
"ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT": "Development"
}
}
Create a New Controller Name liketestControllerthat is usedto create a list and get value in swagger.
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace JWTSwaggerPracticalExam.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class TestController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
[Authorize]
[Route("Get")]
public ActionResult> Get()
{
Return New String { raj, xyz , harsh };
}
}
Add new model Name Like UserData, this Model is set with user name and password. When we enter the username and password in the swagger, that time data would be verified here and the data of UserDatais passed to the Controller. And then the Controller checks the condition whether the user is valid or not.If valid, then it returnswith statementlike “user is valid” otherwise returns “user is not valid”.
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc
namespace JWTSwaggerPracticalExam.Models
{
public class UserData
{
public string username { get; set; }
public string password { get; set; }
}
}
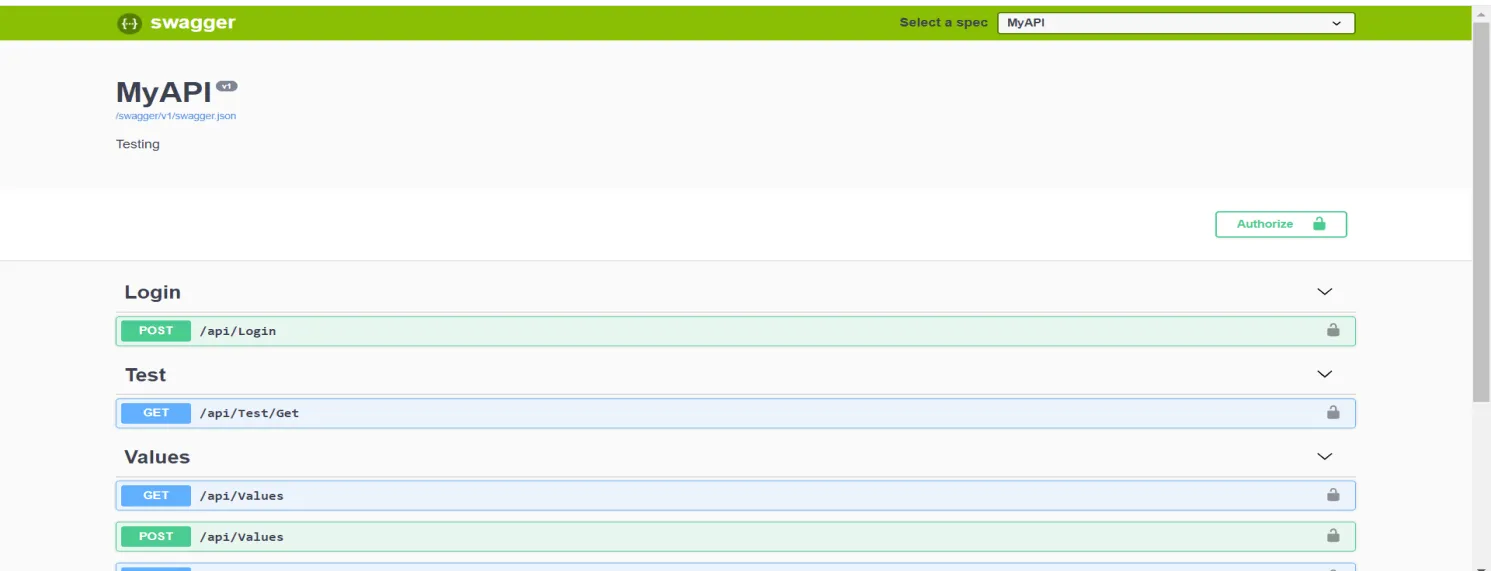
3. Now Run the Project,you will get the swagger UI as shown below
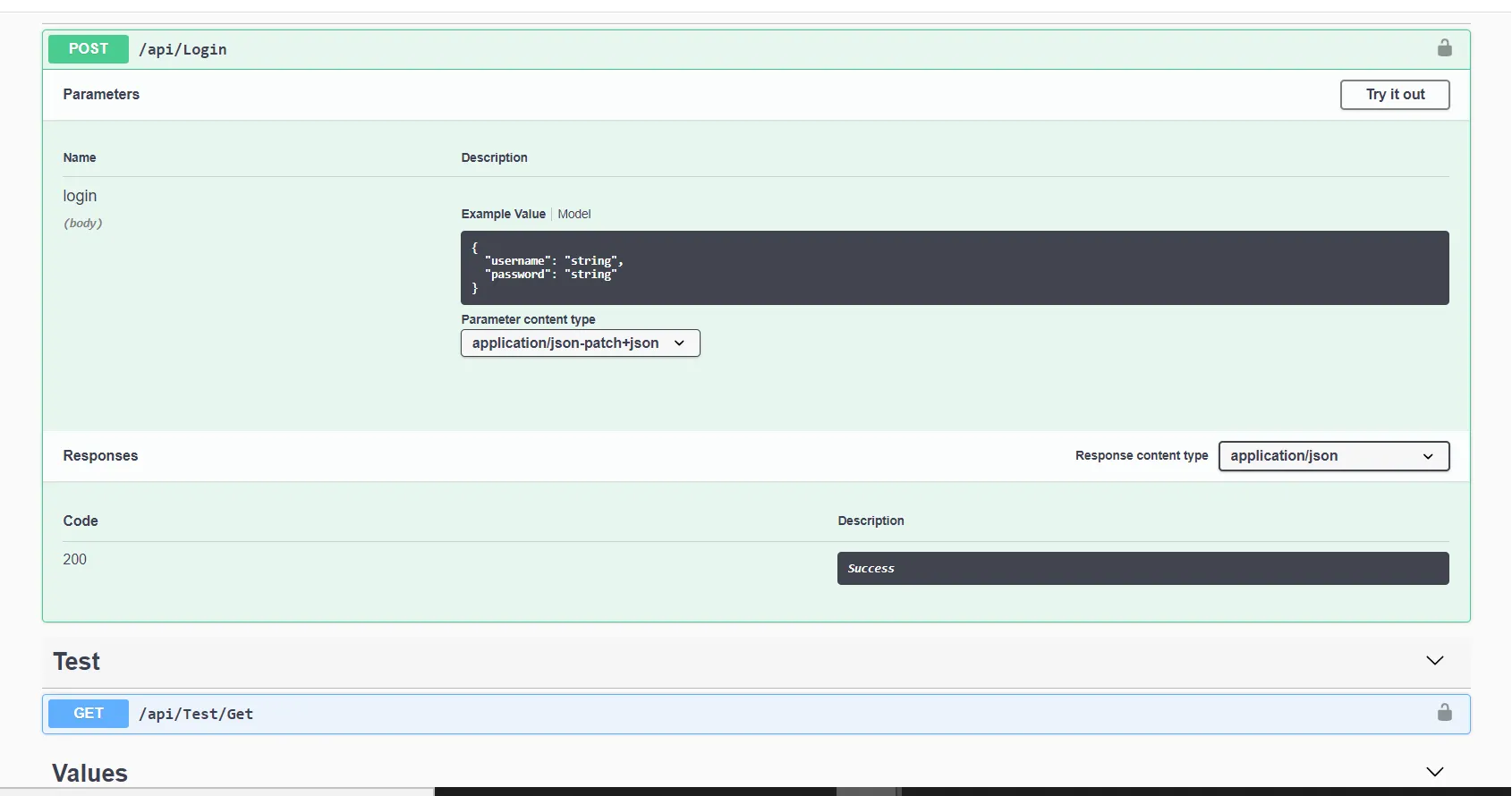
After that, click on login and click on try it out. Now insert username and password, if both are the correct then it returns200 code and success.
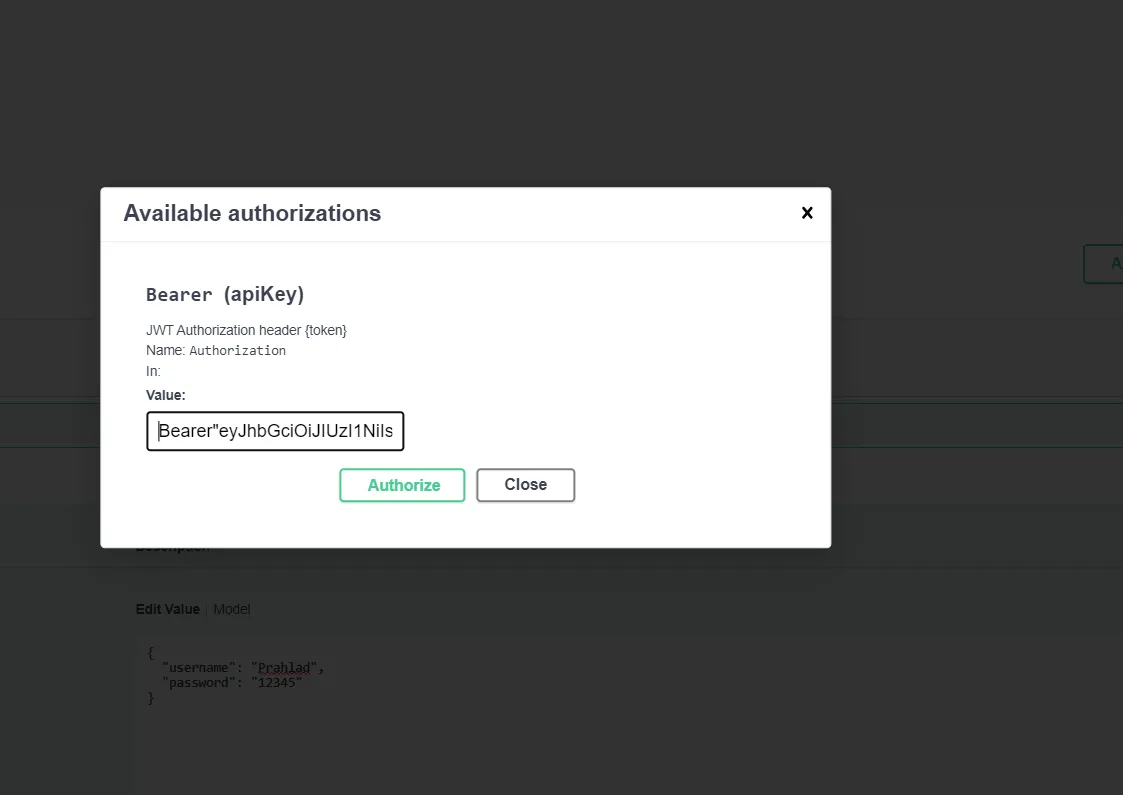
After Generating token copy the token and paste into the authentication Like Bearer=” Paste The Token Here”,
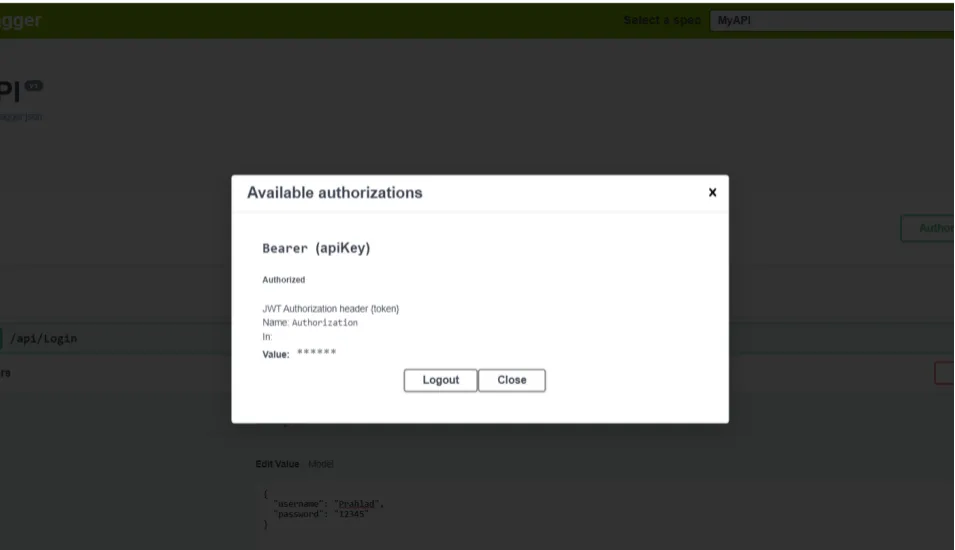
If a token is valid then we get successfully Logged in otherwise it showsauthentication failed401 and Unauthorized error occurred,
You can download the project from below link :
https://github.com/tejassolanki22/JWTSwaggerProject/tree/JWTSwaggerPracticle
After Downloading the project, Unzip the file and open the solution in visual studio 2017 or 2019 and add the Swashbuckle Package and run the Project.Here you will see the API URL. Change this URL and write /Swagger then click on the login method and try it.
Wants to Talk with Our Highly Skilled .Net Developer?
Contact Now
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned how Asp.Net Swagger works and how a web service can reply to web requests from clients such as browsers. Once you understand the needed steps, then it becomes easier to understand the advanced level of Swagger and tools.